recorders

35 SERIES HN35PLUS HN35PLUS MPC*
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
Introducing Honeywell’s 35 Series HN35 NVRs, a robustly-featured,
cost-effective, NDAA Section 889 compliant NVR solution delivering
4K HD (UHD) video resolution perfect for small/medium businesses
and enterprises. Choose a 8, 16 or 32 channel NVR with multiple hard
drive options and up to 20 TB (2 bays) or 40 TB (4 bays) of internal
storage for a flexible solution that grows with your business.

8* / 16* / 32 Ch 4K Embedded NVR
Introducing Honeywell’s 35 Series HN35 NVRs, a robustly-featured,
cost-effective, NDAA Section 889 compliant NVR solution delivering
4K HD (UHD) video resolution perfect for small/medium businesses
and enterprises. Choose a 8, 16 or 32 channel NVR with multiple hard
drive options and up to 20 TB (2 bays) or 40 TB (4 bays) of internal
storage for a flexible solution that grows with your business.
FULLY-FEATURED NVRS
- View 1 to 32 channels simultaneously with synchronized real-time playback (depending on decoding capacity and recording resolution)
- Up to 8 MP (4K) Ultra HD (UHD) resolution live view and playback
- Supports H.265 HEVC, H.264, Smart Codec
- De-warp fisheye camera (HC30WF5R1) video, Honeywell Smart Viewer (HSV) MS Windows® desktop and HSV Mobile App for 360-degree situational awareness
- Supported alarms from 35 Series Cameras to NVR: Crowd, Multi Loitering, Intrusion, Tampering, Motion and Smart Motion Detection (SMD)
- Two-way audio/push notification
DYNAMIC, ACCESSIBLE MONITORING
- Global P2P service with reliable connection and mobile apps for both Apple® and Android™ devices for anytime, anywhere access
- MAXPRO Cloud (MPC)* and P2P integration to manage remote viewing and alarm management
CONVENIENT, FLEXIBLE STORAGE OPTIONS
- Internal storage supports 4 HDDs expandable up to 40 TB (10 TB per drive)
- Store video clips and snapshots to external storage, such as USB device on local side or PC client on web side
MAXPRO CLOUD READY
- Integrated security with MAXPRO Cloud – Access, Intrusion, and Video for small to medium businesses/enterprises with multi-site locations who want Cloud-based flexibility to manage their security
- 8 or 16 Ch NDAA compliant NVRs with flexible storage options
- Remote firmware updates
- Monitor camera and NVR health status
- Push notifications of events from NVR
- Cloud storage for video event and alarms
SECURE AND COMPLIANT SOLUTION
- For use as part of video systems which comply with NDAA Section 889
- The TPM (Trusted Platform Module) provides end-to-end stream and command encryption through integrated cryptographic keys
- Together with 35 Series cameras, provides an end-to-end encrypted solution with video streaming and control encrypted between NVR and web client/viewer/mobile app
- PCI-DSS compliance
- Secure boot feature combined with Honeywell cybersecurity standards helps ensure data protection
EASY TO SETUP AND USE
- Plug and play feature together with 35 Series cameras for rapid and simple setup
- All channels PoE, making it easy to use while also reducing total cost of ownership
- Intuitive NVR design, quick installation wizard, and easy-to-understand installation guide for fast and easy setup
FEATURES
- H.265/H.264
- HDMI/VGA simultaneous video output
- USB ports support Keyboard and Mouse
- Supports recording a video clip of events for distribution
- Supports uploading still images at the time of the event through email
- Supports visual or auditory notifications such as a flashing light, bell, or siren
- Supports alarm input and alarm output
- Supports sending events through email, FTP, alarm out or push notification
- Configurable to automatically detect and respond to motion in the scene, alarm inputs, and network failure or tampering
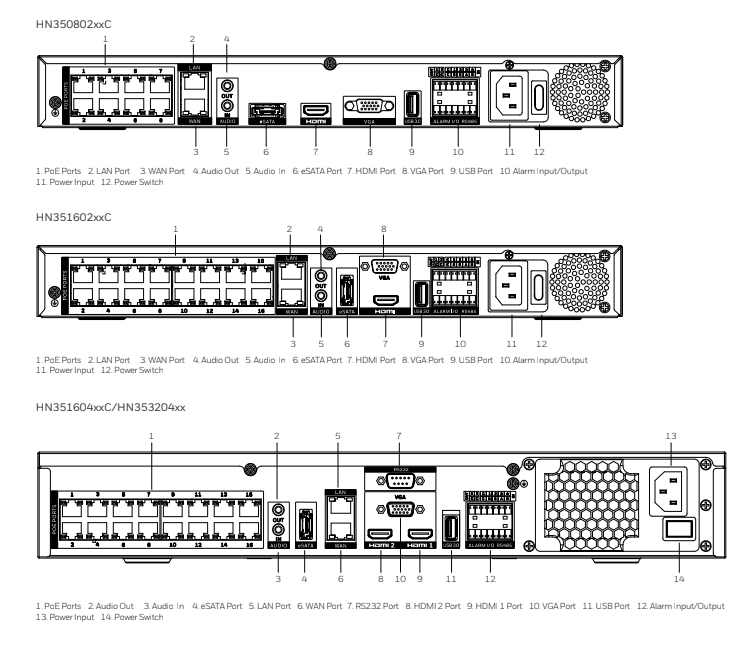
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
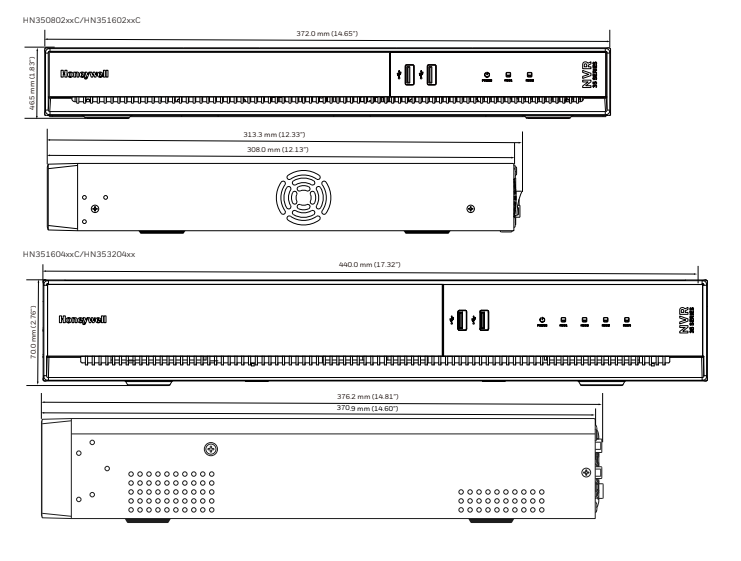
DIMENSIONS
specifications
SYSTEM
VIDEO
AUDIO
DISPLAY
VIDEO DETECTION AND ALARMS
RECORDING
STORAGE
PLAYBACK AND BACKUP
ENVIRONMENTAL
ELECTRICAL
NETWORK
AUXILIARY INTERFACE
PHYSICAL
REGULATORY
RECOMMENDED CAMERAS
Request a Quote
Learn More From
Frequently Asked Questions
Multimode fiber commonly comes in 50/125 μm or 62.5/125 μm core/cladding dimensions, with bandwidth capacities ranging from 200 MHz to 2 GHz, depending on the grade. Multimode systems typically support transmission distances of up to 5 km, making them suitable for short- to medium-range applications.
In contrast, singlemode fiber—usually 9–10/125 μm—offers significantly lower attenuation and effectively unlimited bandwidth, supporting links over 150 to 200 km, especially when paired with optical amplifiers and advanced transceivers.
While singlemode fiber is less expensive per meter, its associated transceivers and equipment tend to cost more than their multimode counterparts. That said, singlemode devices are generally compatible with both singlemode and multimode fiber, whereas multimode equipment works only with multimode fiber.
Let me know if you’d like this turned into a quick-reference table or visual comparison—it’d make a solid inclusion for a fiber deployment guide.
The link budget is the difference between the transmitter’s output power and the receiver’s sensitivity. This budget must account for all signal losses along the path, including:
- Fiber attenuation due to the transmission medium
- Connector losses, such as those at patch panels or equipment interfaces
- Splice losses from mechanical or fusion joints
- Link margin, which provides a buffer for unforeseen variations
The link margin typically ranges from 2–3 dB in tightly controlled environments to up to 10 dB in more variable conditions. It is designed to accommodate:
- Component aging (e.g., light sources may degrade and lose up to 3 dB over time)
- Temperature variations affecting transmitter output or receiver sensitivity (up to 3 dB may be needed for thermal fluctuations)
- Physical cable damage and repair-induced losses (usually minor, but more relevant in harsh or industrial settings)
Always design your system for worst-case scenarios to ensure reliability. However, don’t overlook the best-case condition either—some optical receivers may exhibit erratic behavior if the incoming signal is too strong.
First, verify the optical signal strength along the link. Use an optical power meter to measure the received power at the fiber’s end point. Typical transmit levels range from –8 dBm to –15 dBm, while the receiver sensitivity is around –31 dBm, giving you a link budget of approximately 16 dB. This margin supports transmission distances of up to 10 km on singlemode fiber and about 3–5 km on multimode fiber.
If the measured power falls below the receiver sensitivity, there’s a strong likelihood of issues with the installed fiber. Ideally, initial OTDR readings should have flagged such faults.
If not, inspect the patch cords currently in use for possible defects or misalignment. A frequent oversight is the use of mismatched patch cords.
Multimode fiber types are classified by the ISO/IEC 11801 standard into five main categories: OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5. Each type differs in core size, bandwidth, supported data rates, and maximum transmission distances. Here’s a quick breakdown:
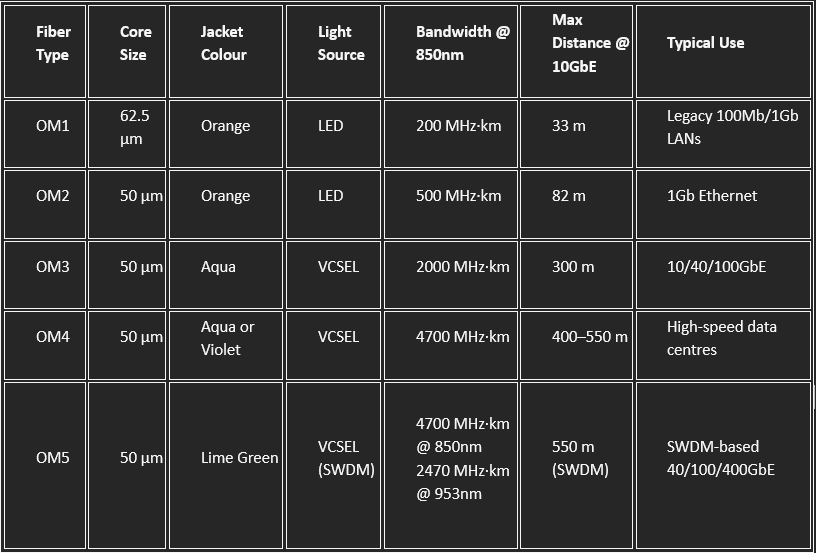
- OM3 and OM4 are laser-optimized and widely used in modern data centers.
- OM5 supports shortwave wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM), enabling multiple wavelengths over a single fiber for higher capacity.
- All OM types are backward compatible in terms of connectors, but mixing core sizes (e.g., OM1 with OM3) can cause performance issues.
