edge switches

5-port 10/100/1000Mbit/s Easy webmanaged Gigabit Ethernet Switch with 4x PoE Outputs (802.3af)
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
- 5-port 10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Switch with 4x PoE Output (802.3af)
- PoE Budget approximately 70W for a maximum of 4 devices, supports up to 30W per port IEEE802.3at
- Easy Smart-Managed
- Fanless Design

5-port 10/100/1000Mbit/s Easy webmanaged Gigabit Ethernet Switch with 4x PoE Outputs (802.3af)
- 5-port 10/100/1000Mbps Gigabit Ethernet Switch with 4x PoE Output (802.3af)
- PoE Budget approximately 70W for a maximum of 4 devices, supports up to 30W per port IEEE802.3at
- Easy Smart-Managed
- Fanless Design
Description: The new ALLNET ALL-SG8245PM switch provides a robust foundation for a networked workplace. Featuring 5 gigabit ports that are backward-compatible, it seamlessly integrates computers, printers, access points, and other devices into your network reliably. The ALL-SG8245PM also supports Power over Ethernet (PoE) with its 4 PoE ports (IEEE802.3af), eliminating the need for additional power cables for connected devices.
Ensuring silent operation, crucial for workplace environments, the ALL-SG8245PM incorporates a fanless design. It offers enhanced usability with its smart managed capabilities, allowing configurations for VLAN (Virtual LAN) and QoS (Quality of Service), among other features
specifications
CERTIFICATION AND SHARED
- Switch Type:
- Layer 2-Switch, Web easy smart managed
- Standards:
- IEEE802.3 10BASE-T
- IEEE802.3u 100BASE-TX
- IEEE802.3ab 1000BASE-T
- IEEE802.3az EEE
- IEEE802.3ad Link Aggregation
- IEEE802.1q VLAN
- IEEE802.1p-based QoS
- Switching Ports:
- 5x RJ45 10/100/1000BaseT(X)
- 4x PoE IEEE802.3at max. 30W per Port
- Special: 4x PSE Port for PoE Devices
- Uplink: Yes
- Full Duplex Mode: Yes
- Buffer Memory: 1Mbits
- Jumbo Frames:
- 9216 bytes
- MAC Address Table:
- 2K
- Filtering/Forwarding:
- Store-and-Forward
- LED Definitions:
- Power/System: Green LED
- Off: Power off or fail
- On: Power on
- Blinking: System booting up
- PoE Alert: Green LED
- Off: No over PoE max power budget (50W)
- On: Over PoE max power budget (50W)
- RJ 45 Port:
- LINK/ACT: Bi-color LED
- Off: Port disconnected or link fail
- Green on: 1000Mbps connected
- Amber on: 10/100Mbps connected
- Blinking: Sending or receiving data
- PoE:
- Off: PoE power output off
- Green on: PoE power output on
- Layer 2 Basic:
- Port: Auto Negotiation of speed and duplex modes
- Jumbo frame support
- Mirror: Port mirroring both on ingress and egress traffic
- VLAN: 802.1Q VLAN, Port-based VLAN
- LACP: Link Aggregation = IEEE802.3ad
- Multicast: Blocking of unknown multicast traffic
- QoS: IEEE802.1p-based QoS, Port-based QoS
- Scheduling Method: WFQ or SP
- IGMP Snooping:
- Support IGMPv1 Snooping RFC 1122, RFC4541
- Support IGMPv2 Snooping RFC 2236, RFC4541
- Support IGMPv3 Snooping (Partial) RFC 3376
- Security:
- STP / Self Loop Support
- Broadcast Storm Control Support
- Management:
- User Interface: Web-based Management
- User Account System: Password protection
- PoE: PoE power output On/Off management
- Power Input:
- Power-Input: AC to DC external power adapter
- Input: 100~240V AC
- Output: 55VDC / 1.3A
- Housing: Metal/ Desktop
- PoE Output power capacity: Maximum output: 30W per each port
- Additional Features:
- Compliant with IEEE802.3af/at standard, following IEEE802.3at/at to support PoE or PoE+
- Automatically discover the connection of PD device and immediately sends power to it
- Auto disable port if the port current is over 700mA or short happens
- Priority default setting is lower port NO. has high priority
- The maximum power used by power devices is defined by the following classification. When Port works in Auto Mode, the output port power limit will be associated with PD classification Value.
- Follow the standard PSE pin-out standard of Alternative A (MAD-X), which is sending out power over number 1, 2, 3, 6 pins of 8 wires of Ethernet CAT5 UTP cable
- Dimensions and Environmental Conditions:
- Dimensions: 193 x 84 x 26mm
- Operating Temperature: 0 ~ 50 °C
- Operating Humidity: 10% ~ 90% (non-condensing)
- Storage Temperature: -40 ~ 70 °C
- Storage Humidity: 5% ~ 90% (non-condensing)
- Marks:
- CE, FCC EMI class B, ROHS
Zubehör
- **147402 ALLNET PoE Injektor Gigabit ALL0489V3 – 802.3af/at HPoE 30W, IEC-C6 Metallgehäuse
- **99315 ALLNET Switch unmanaged 8 port Gigabit HPoE, 2x PoE+ oder 4x PoE, lüfterlos, internes Netzteil, 19″ ALL8804PoE+
- **90956 ALLNET Switch smart managed 8 Port Gigabit HPoE , 2x PoE+ oder 4x PoE, lüfterlos, internes Netzteil ALL8894WMP
- **93392 ALLNET Switch unmanaged 8 port Gigabit HPoE, 4x PoE+ oder 8x PoE, lüfterlos, internes Netzteil, 19″ ALL8808PoE
- **137466 ALLNET Switch full managed 8 Port Gigabit HPoE + 2 Giga Combo Ports (RJ/SFP) ALL-SG8910PM
- **75932 Patchkabel RJ45 FTP(F/UTP) 0,25m grau, CAT5e, Synergy 21
- **137465 ALLNET Switch full managed 24 Port Gigabit HPoE nach 802.3af und 802.3at incl 2 Giga Combo Ports (RJ/SFP) ALL-SG8926v2PM
- **75939 Patchkabel RJ45 FTP(F/UTP) 0,5m grau, CAT5e, Synergy 21
- **75946 Patchkabel RJ45 FTP(F/UTP) 1,0m grau, CAT5e, Synergy 21
- **75959 Patchkabel RJ45 FTP(F/UTP) 2m grau, CAT5e, Synergy 21
- **75966 Patchkabel RJ45 FTP(F/UTP) 3m grau, CAT5e, Synergy 21
- **75973 Patchkabel RJ45 FTP(F/UTP) 5m grau, CAT5e, Synergy 21
- **75979 Patchkabel RJ45 FTP(F/UTP) 7,5m grau, CAT5e, Synergy 21
- **75986 Patchkabel RJ45 FTP(F/UTP) 10m grau, CAT5e, Synergy 21
- **75992 Patchkabel RJ45 FTP(F/UTP) 15m grau, CAT5e, Synergy 21
- **76029 Patchkabel RJ45, 0,25m grau, CAT5e, S-FTP(SF/UTP), Synergy 21
- **76036 Patchkabel RJ45, 0,5m grau, CAT5e, S-FTP(SF/UTP), Synergy 21
- **76043 Patchkabel RJ45, 1,0m grau, CAT5e, S-FTP(SF/UTP), Synergy 21
- **76056 Patchkabel RJ45, 2m grau, CAT5e, S-FTP(SF/UTP), Synergy 21
- **76063 Patchkabel RJ45, 3m grau, CAT5e, S-FTP(SF/UTP), Synergy 21
- **76070 Patchkabel RJ45, 5m grau, CAT5e, S-FTP(SF/UTP), Synergy 21
- **76077 Patchkabel RJ45, 7,5m grau, CAT5e, S-FTP(SF/UTP), Synergy 21
- **76084 Patchkabel RJ45, 10m grau, CAT5e, S-FTP(SF/UTP), Synergy 21
- **76091 Patchkabel RJ45, 15m grau, CAT5e, S-FTP(SF/UTP), Synergy 21
- **76117 Patchkabel RJ45, CAT6 250Mhz, 0,25m grau, S-STP(S/FTP), Synergy 21
- **76124 Patchkabel RJ45, CAT6 250Mhz, 0,5m grau, S-STP(S/FTP), Synergy 21
- **76133 Patchkabel RJ45, CAT6 250Mhz, 1,0m grau, S-STP(S/FTP), Synergy 21
- **76151 Patchkabel RJ45, CAT6 250Mhz, 2m grau, S-STP(S/FTP), Synergy 21
- **76160 Patchkabel RJ45, CAT6 250Mhz, 3m grau, S-STP(S/FTP), Synergy 21
- **76169 Patchkabel RJ45, CAT6 250Mhz, 5m grau, S-STP(S/FTP), Synergy 21
- **76178 Patchkabel RJ45, CAT6 250Mhz, 7,5m grau, S-STP(S/FTP), Synergy 21
- **76187 Patchkabel RJ45, CAT6 250Mhz,10m grau, S-STP(S/FTP), Synergy 21
- **76196 Patchkabel RJ45, CAT6 250Mhz,15m grau, S-STP(S/FTP), Synergy 21
- **140955 TP(RJ45) POE-Tester, at/af, Endspan/Midspan, standard, Synergy 21
Request a Quote
Learn More From
Frequently Asked Questions
Multimode fiber commonly comes in 50/125 μm or 62.5/125 μm core/cladding dimensions, with bandwidth capacities ranging from 200 MHz to 2 GHz, depending on the grade. Multimode systems typically support transmission distances of up to 5 km, making them suitable for short- to medium-range applications.
In contrast, singlemode fiber—usually 9–10/125 μm—offers significantly lower attenuation and effectively unlimited bandwidth, supporting links over 150 to 200 km, especially when paired with optical amplifiers and advanced transceivers.
While singlemode fiber is less expensive per meter, its associated transceivers and equipment tend to cost more than their multimode counterparts. That said, singlemode devices are generally compatible with both singlemode and multimode fiber, whereas multimode equipment works only with multimode fiber.
Let me know if you’d like this turned into a quick-reference table or visual comparison—it’d make a solid inclusion for a fiber deployment guide.
The link budget is the difference between the transmitter’s output power and the receiver’s sensitivity. This budget must account for all signal losses along the path, including:
- Fiber attenuation due to the transmission medium
- Connector losses, such as those at patch panels or equipment interfaces
- Splice losses from mechanical or fusion joints
- Link margin, which provides a buffer for unforeseen variations
The link margin typically ranges from 2–3 dB in tightly controlled environments to up to 10 dB in more variable conditions. It is designed to accommodate:
- Component aging (e.g., light sources may degrade and lose up to 3 dB over time)
- Temperature variations affecting transmitter output or receiver sensitivity (up to 3 dB may be needed for thermal fluctuations)
- Physical cable damage and repair-induced losses (usually minor, but more relevant in harsh or industrial settings)
Always design your system for worst-case scenarios to ensure reliability. However, don’t overlook the best-case condition either—some optical receivers may exhibit erratic behavior if the incoming signal is too strong.
First, verify the optical signal strength along the link. Use an optical power meter to measure the received power at the fiber’s end point. Typical transmit levels range from –8 dBm to –15 dBm, while the receiver sensitivity is around –31 dBm, giving you a link budget of approximately 16 dB. This margin supports transmission distances of up to 10 km on singlemode fiber and about 3–5 km on multimode fiber.
If the measured power falls below the receiver sensitivity, there’s a strong likelihood of issues with the installed fiber. Ideally, initial OTDR readings should have flagged such faults.
If not, inspect the patch cords currently in use for possible defects or misalignment. A frequent oversight is the use of mismatched patch cords.
Multimode fiber types are classified by the ISO/IEC 11801 standard into five main categories: OM1, OM2, OM3, OM4, and OM5. Each type differs in core size, bandwidth, supported data rates, and maximum transmission distances. Here’s a quick breakdown:
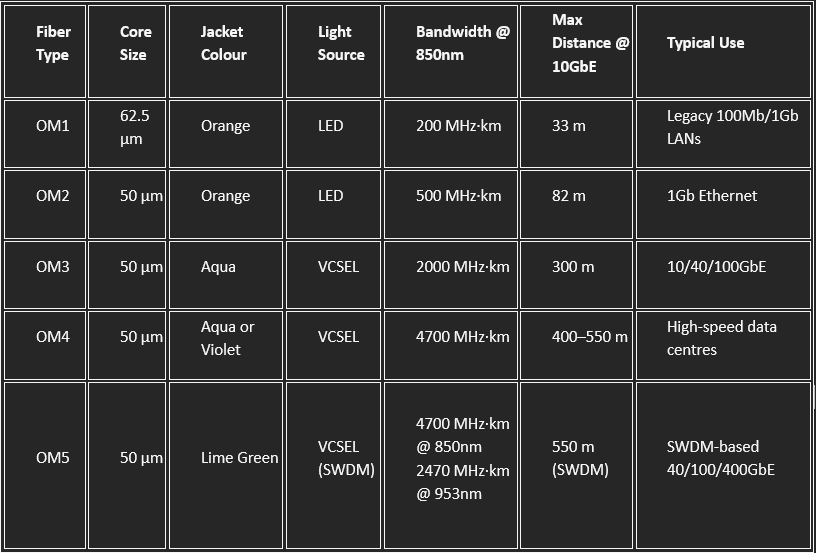
- OM3 and OM4 are laser-optimized and widely used in modern data centers.
- OM5 supports shortwave wavelength division multiplexing (SWDM), enabling multiple wavelengths over a single fiber for higher capacity.
- All OM types are backward compatible in terms of connectors, but mixing core sizes (e.g., OM1 with OM3) can cause performance issues.
